Virtual Machine Actions
After creating a virtual machine (VM), you may need to perform various actions to manage its lifecycle. This section covers the available VM actions and how to use them effectively.
Main VM Actions
- Console - Access the VM's console for direct interaction.
- Reboot – Restart the VM gracefully.
- Shut down – Shut down the VM gracefully.
- Hard reboot – Force restart the VM (like pressing reset).
- Power off – Force power off the VM (like cutting the power).
- Shelve – Temporarily store the VM and free up resources.
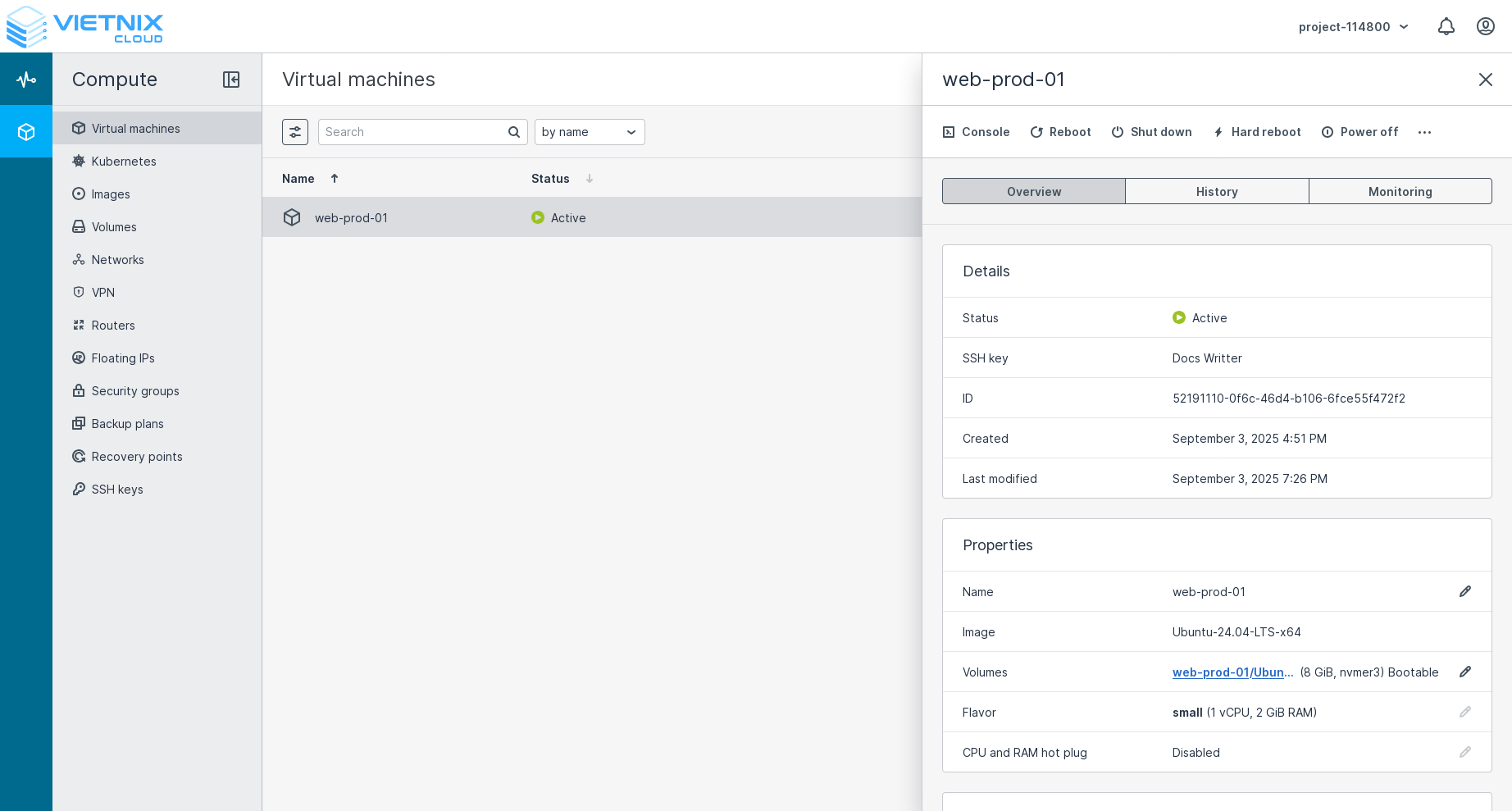 Select the VM you want to control, then choose the desired action from the menu
Select the VM you want to control, then choose the desired action from the menu
Console
Console allows you to access the VM's console directly from the Vietnix Cloud Console. This is useful for troubleshooting, performing maintenance tasks, or interacting with the VM when remote access is unavailable.
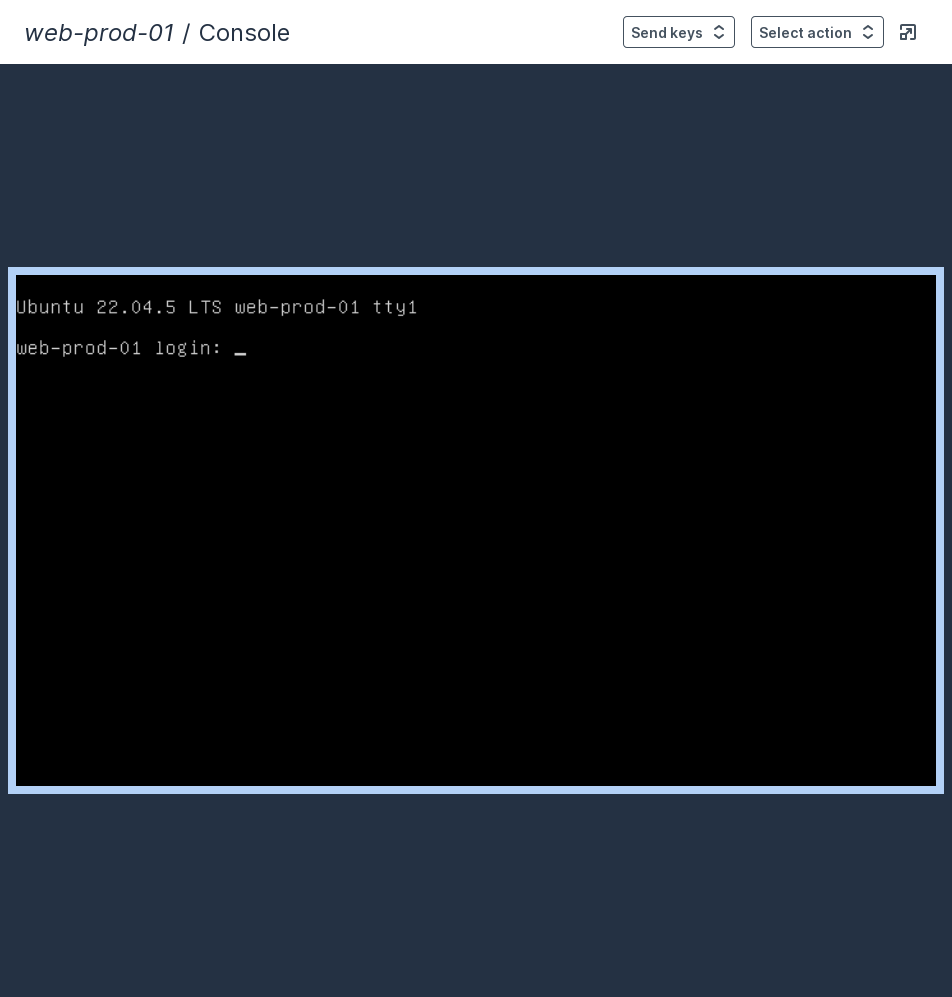
We support remote access to the VM console. You can learn how to Remote to the VM at Remote Access.
Reboot
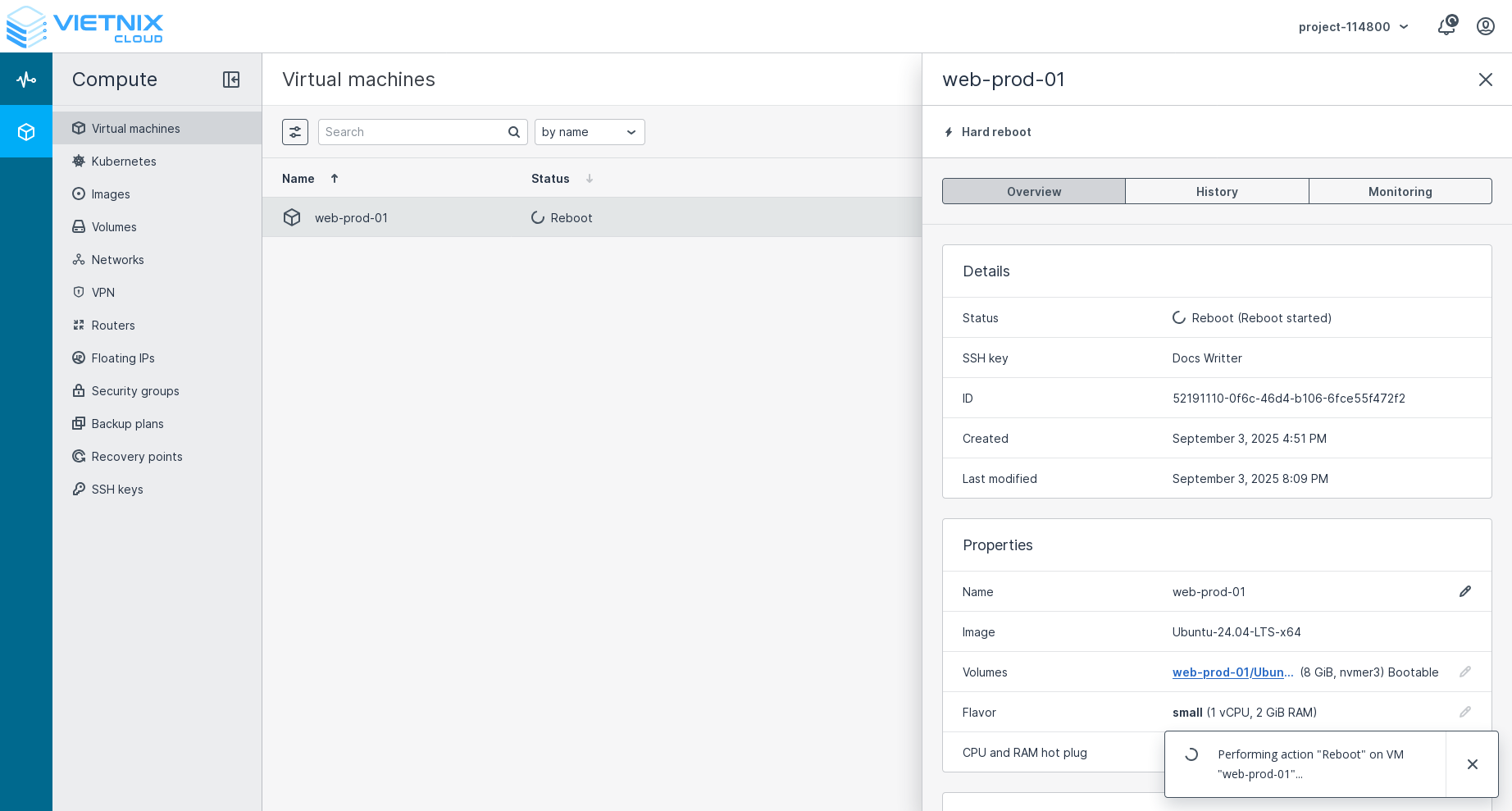 Press the reboot button. This action will reboot the VM. It will take a few moments for the VM to come back online.
Press the reboot button. This action will reboot the VM. It will take a few moments for the VM to come back online.
The reboot action executes immediately witho ut any confirmation dialog. Be sure you want to reboot the VM before clicking this button.
Shut down
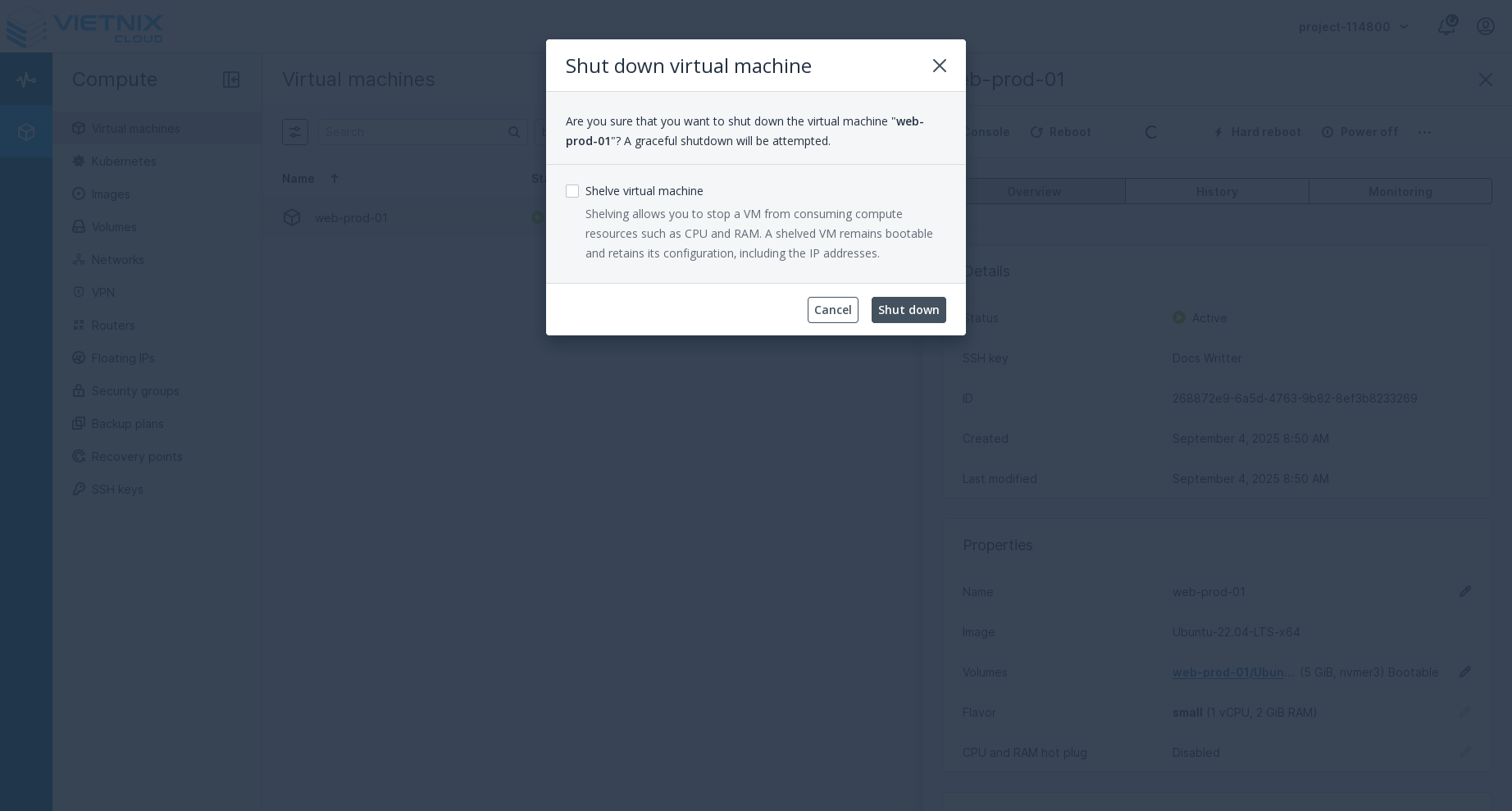 Press the shut down button. This action will gracefully shut down the VM's operating system. Unlike the reboot action, shut down requires confirmation through a dialog box before proceeding.
Press the shut down button. This action will gracefully shut down the VM's operating system. Unlike the reboot action, shut down requires confirmation through a dialog box before proceeding.
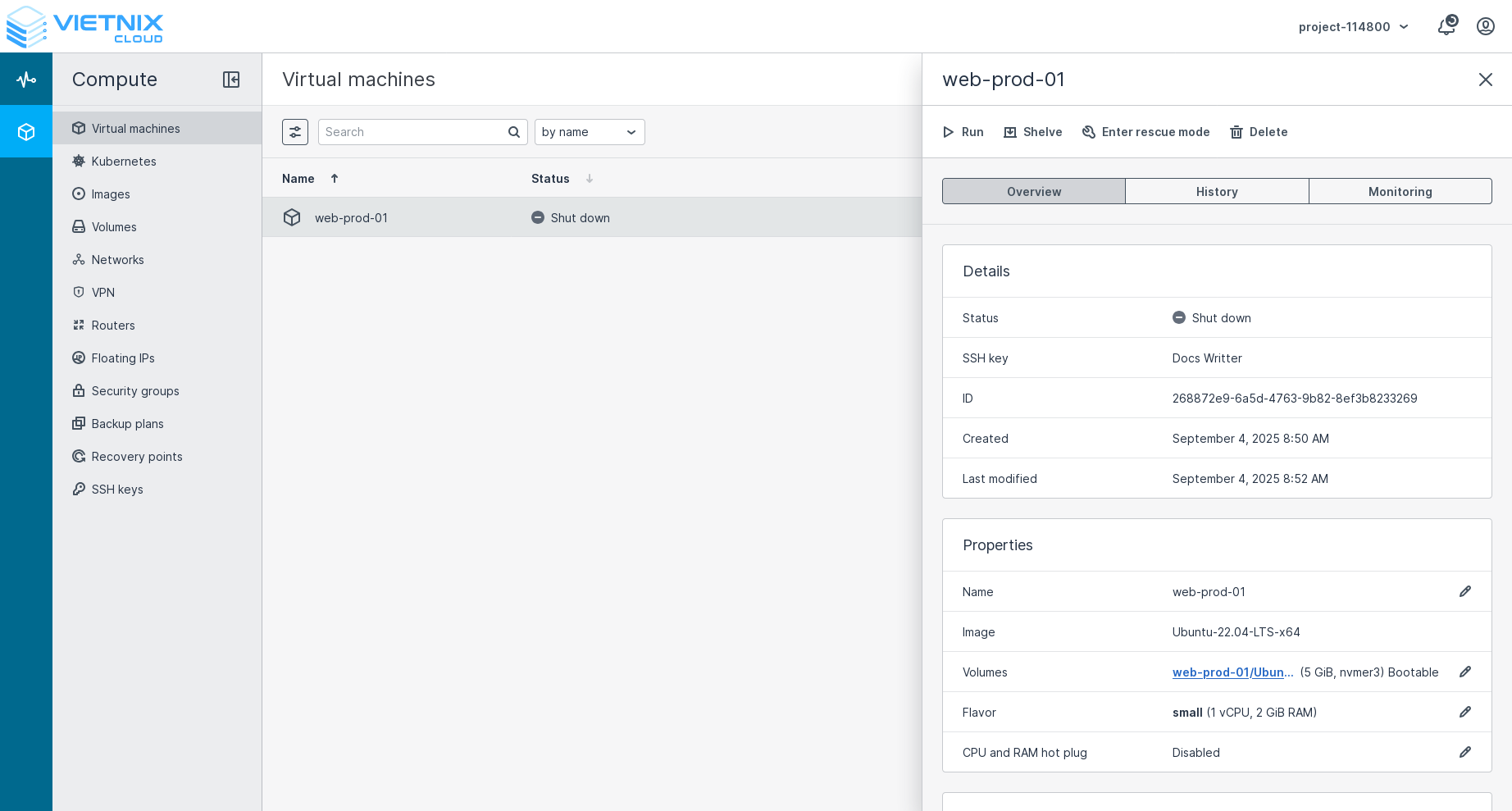 After the VM was shut down, you can run it again, shelve or enter rescue mode.
After the VM was shut down, you can run it again, shelve or enter rescue mode.
Hard reboot
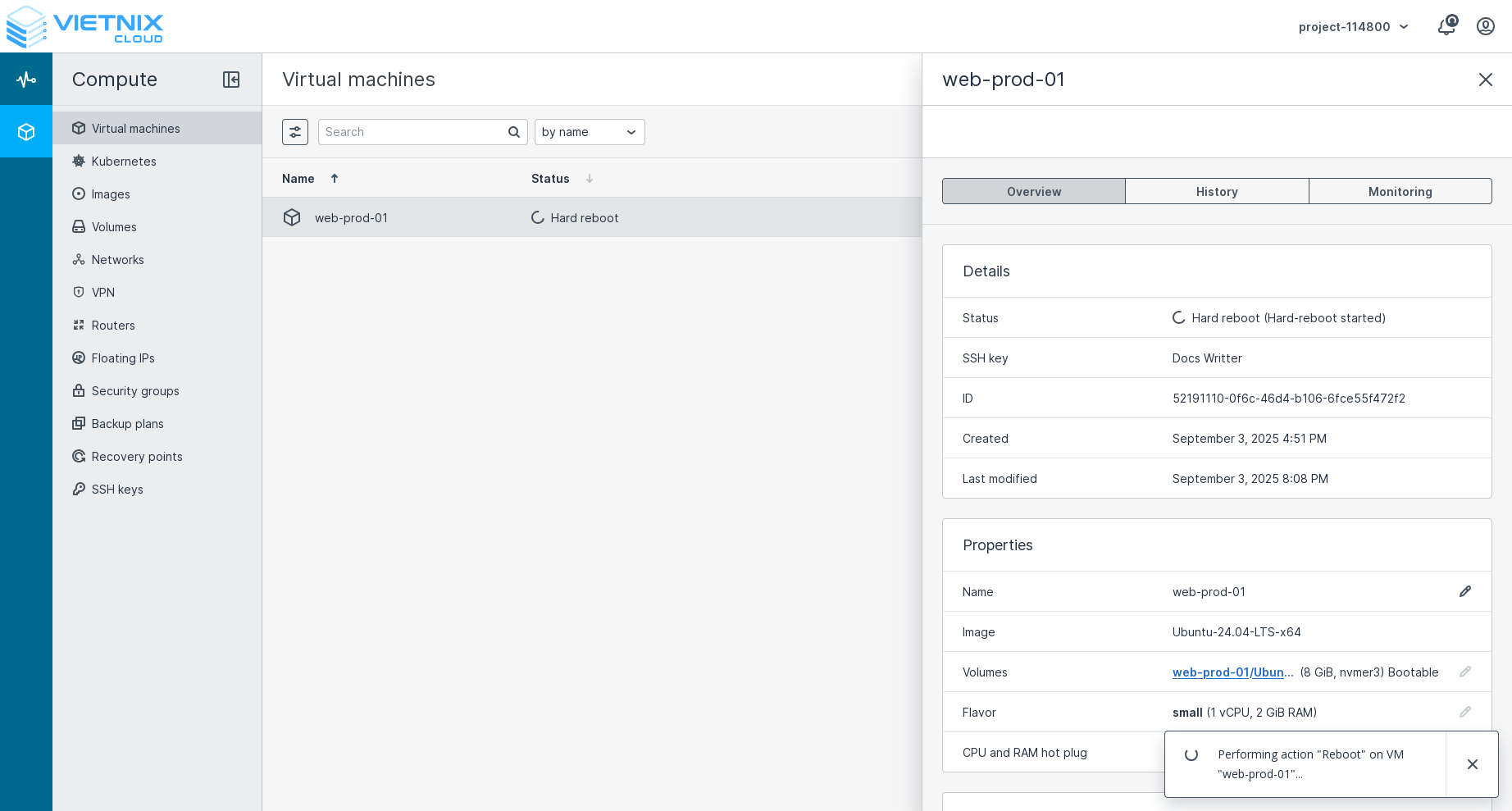 Pressed the hard reboot button. This action will forcefully restart the VM without shutting it down gracefully. It is similar to pressing the reset button on a physical machine. Use this option if the VM is unresponsive and cannot be rebooted normally.
Pressed the hard reboot button. This action will forcefully restart the VM without shutting it down gracefully. It is similar to pressing the reset button on a physical machine. Use this option if the VM is unresponsive and cannot be rebooted normally.
The hard reboot action executes immediately without any confirmation dialog. Be sure you want to hard reboot the VM before clicking this button.
Power off
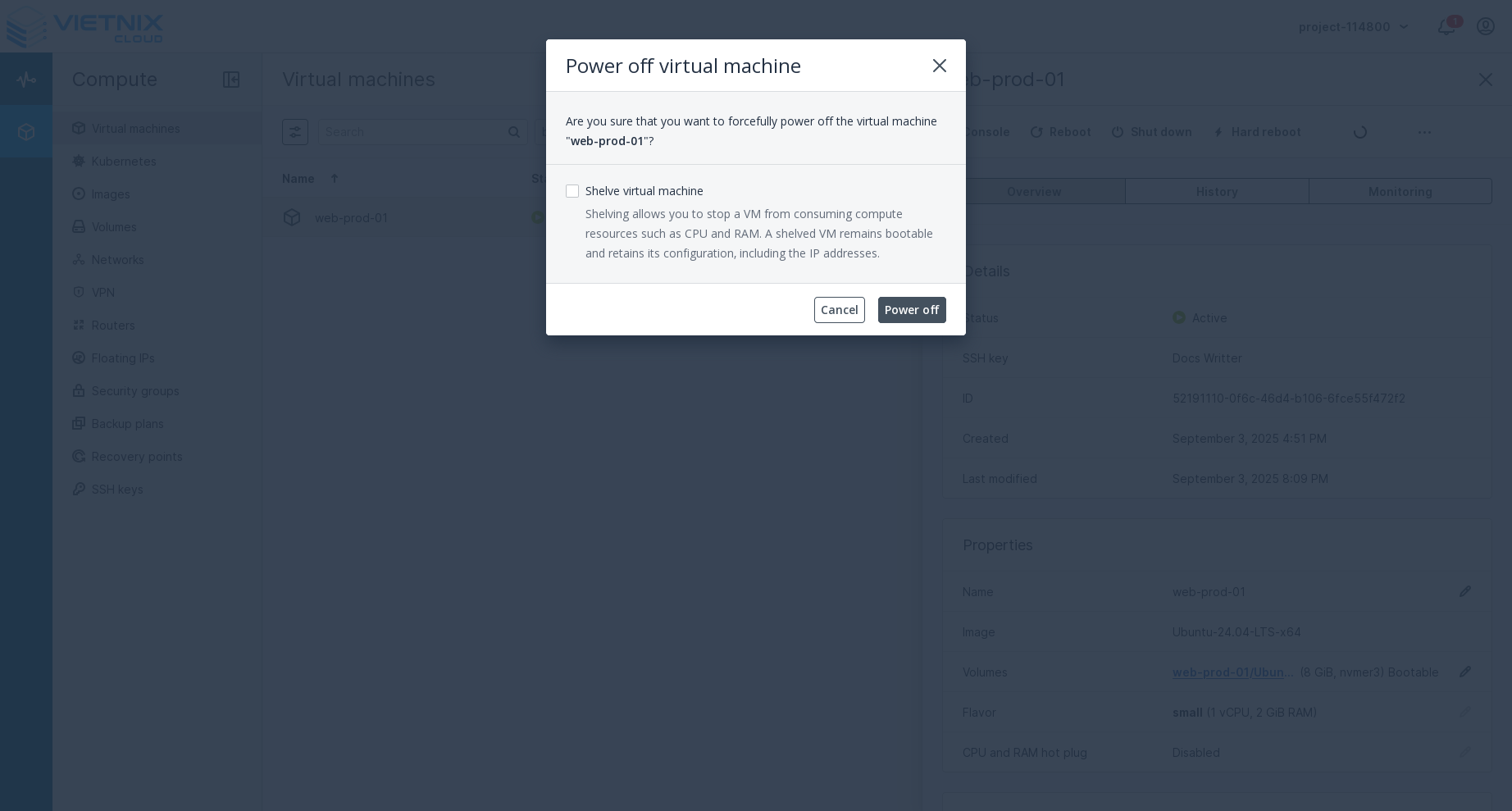 Pressed the power off button. This action will forcefully power off the VM without shutting it down gracefully. It is similar to cutting the power to a physical machine. Use this option if the VM is unresponsive and cannot be shut down normally.
Pressed the power off button. This action will forcefully power off the VM without shutting it down gracefully. It is similar to cutting the power to a physical machine. Use this option if the VM is unresponsive and cannot be shut down normally.
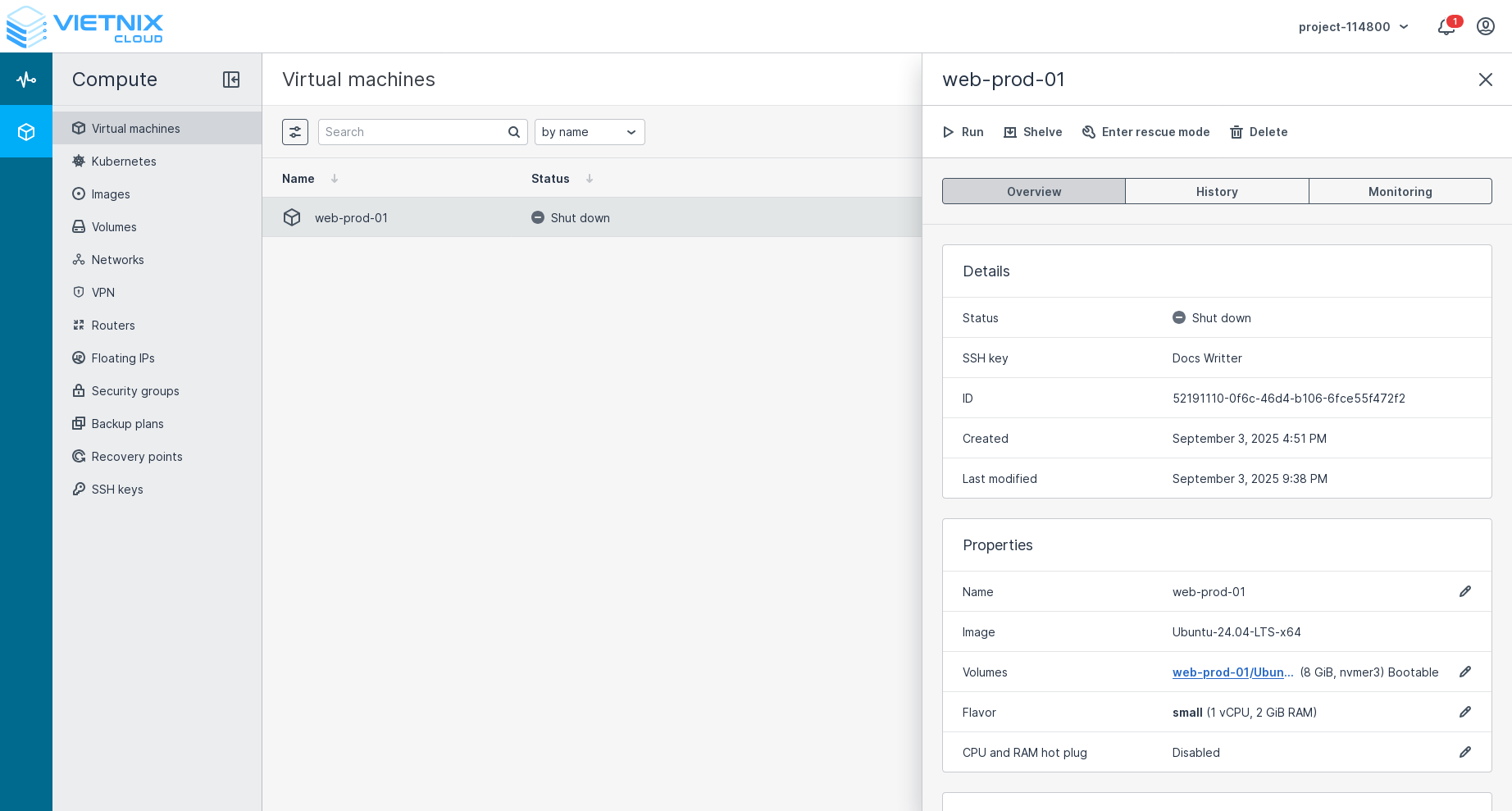 After the VM is powered off, you can run it again, shelve or enter rescue mode.
After the VM is powered off, you can run it again, shelve or enter rescue mode.
Shelve
Shelving allows you to stop a VM from consuming compute resources such as CPU and RAM. A shelved VM remains bootable and retains its configuration, including the IP addresses.
You can shelve a VM with options to shelve when you shut down or power off the VM, or shelve it after the VM has been shutdown.
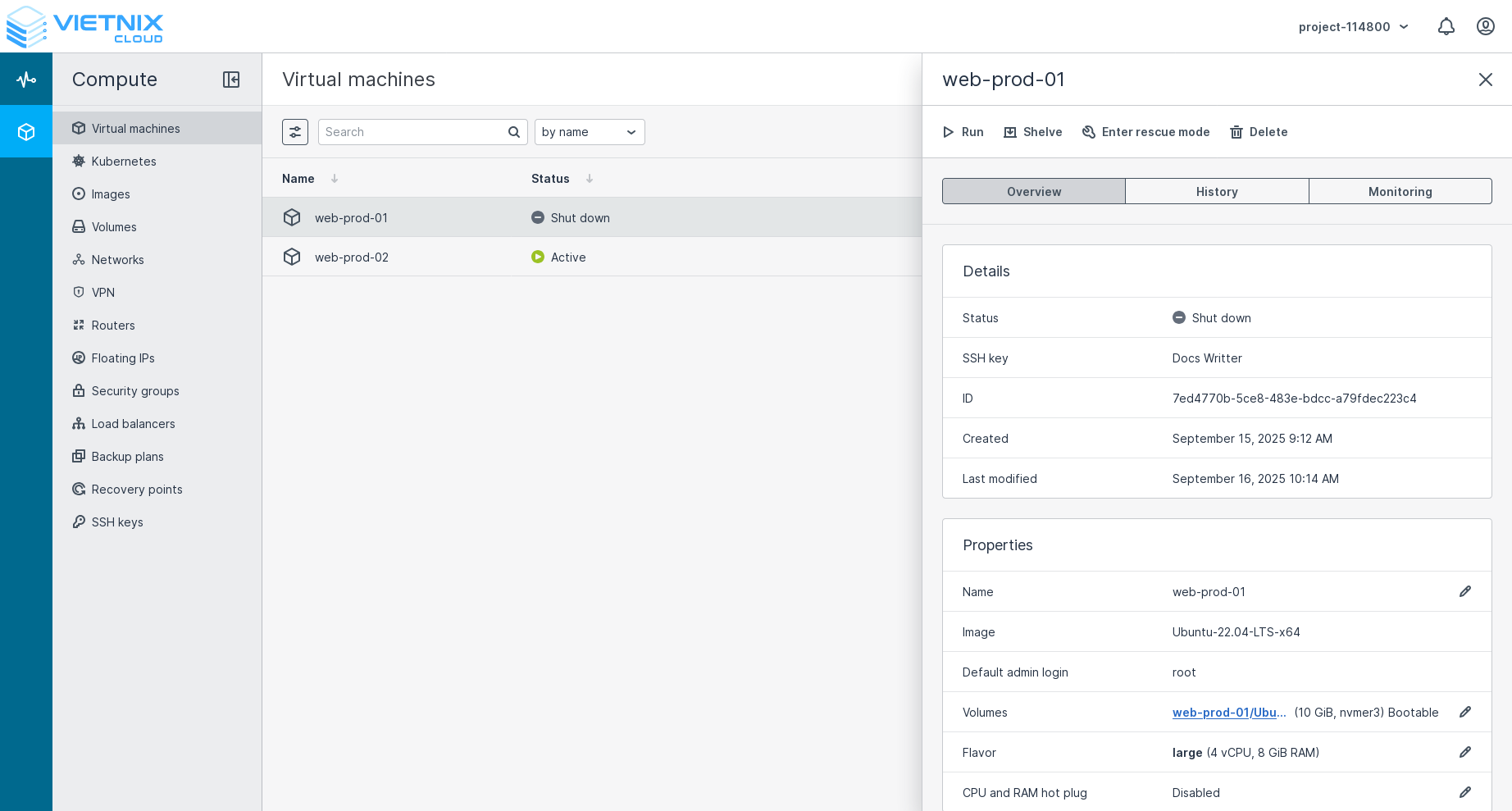
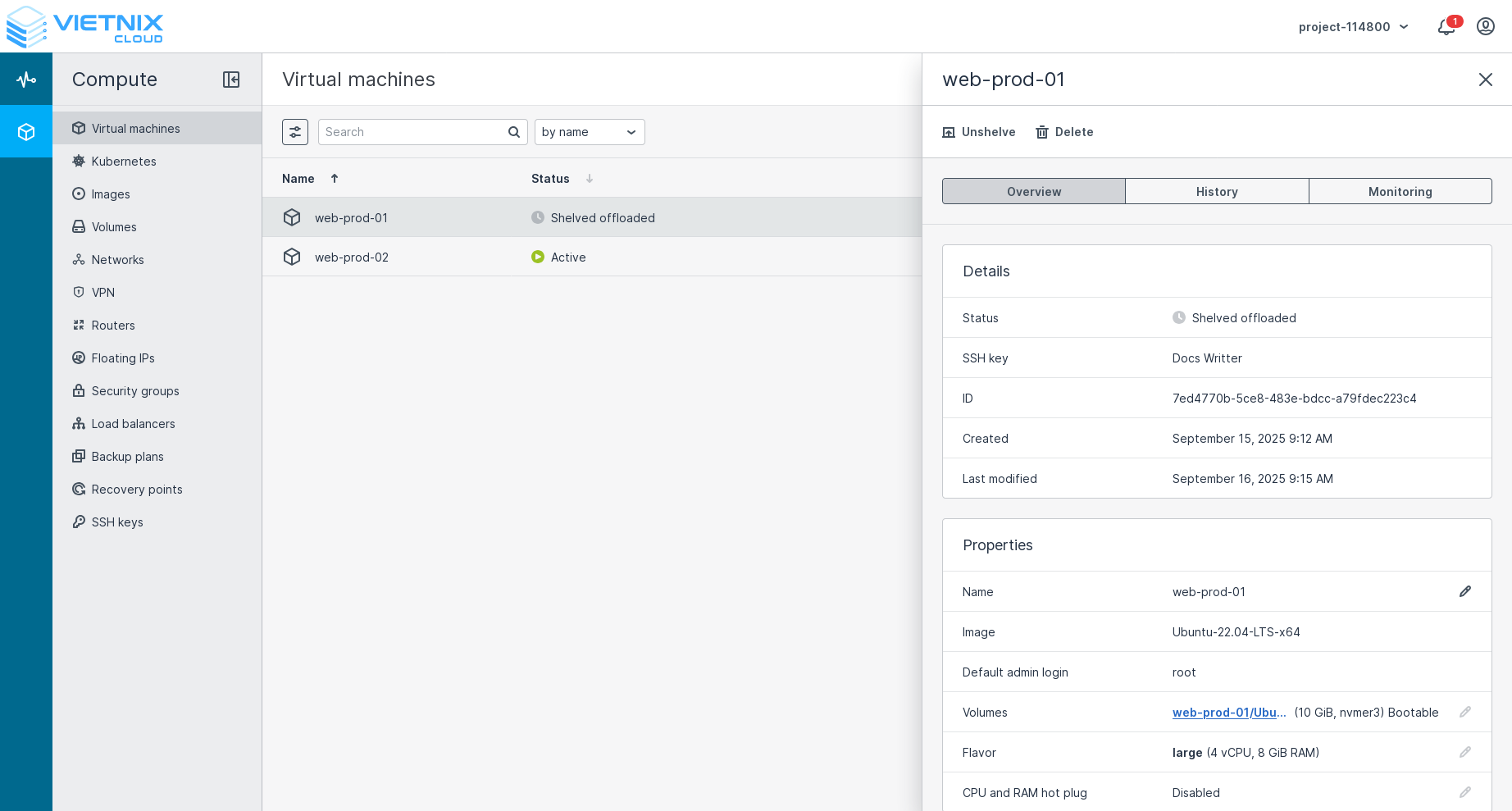
A shelved VM prevents you from performing certain actions to keep it in a consistent state and avoid data loss such as:
- Run
- Enter rescue mode
- Network actions (Attach/detach network, Change security groups, etc.)
- Create snapshot
- Revert snapshot
- Attach/detach volume
Comparison of VM Control Actions
The following table compares the different VM control actions:
| Action | Description | Method | Use Case | Confirmation Required | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reboot | Restarts the VM | Graceful - proper OS shutdown and restart | Regular maintenance, applying updates | No | Low |
| Shut down | Shuts down the VM | Graceful - proper OS shutdown | When VM is not needed temporarily | Yes | Low |
| Hard reboot | Forces VM to restart | Forceful - similar to pressing reset button | When VM is unresponsive to normal reboot | No | Medium |
| Power off | Forces VM to power off | Forceful - similar to cutting power | When VM cannot be shut down normally | Yes | High |
| Shelve | Stops VM from consuming resources | Graceful - saves state and configuration | When VM is not needed for an extended period | No | Low |
Forceful actions (Hard reboot and Power off) may lead to data loss or file system corruption if performed while disk operations are in progress.
Additional VM Actions
- Set password – Set or change the password for the VM.
- Enter rescue mode – Boot the VM into rescue mode for troubleshooting.
- Download console log – Get the VM console logs for debugging.
- Delete – Permanently delete the VM.
Set password
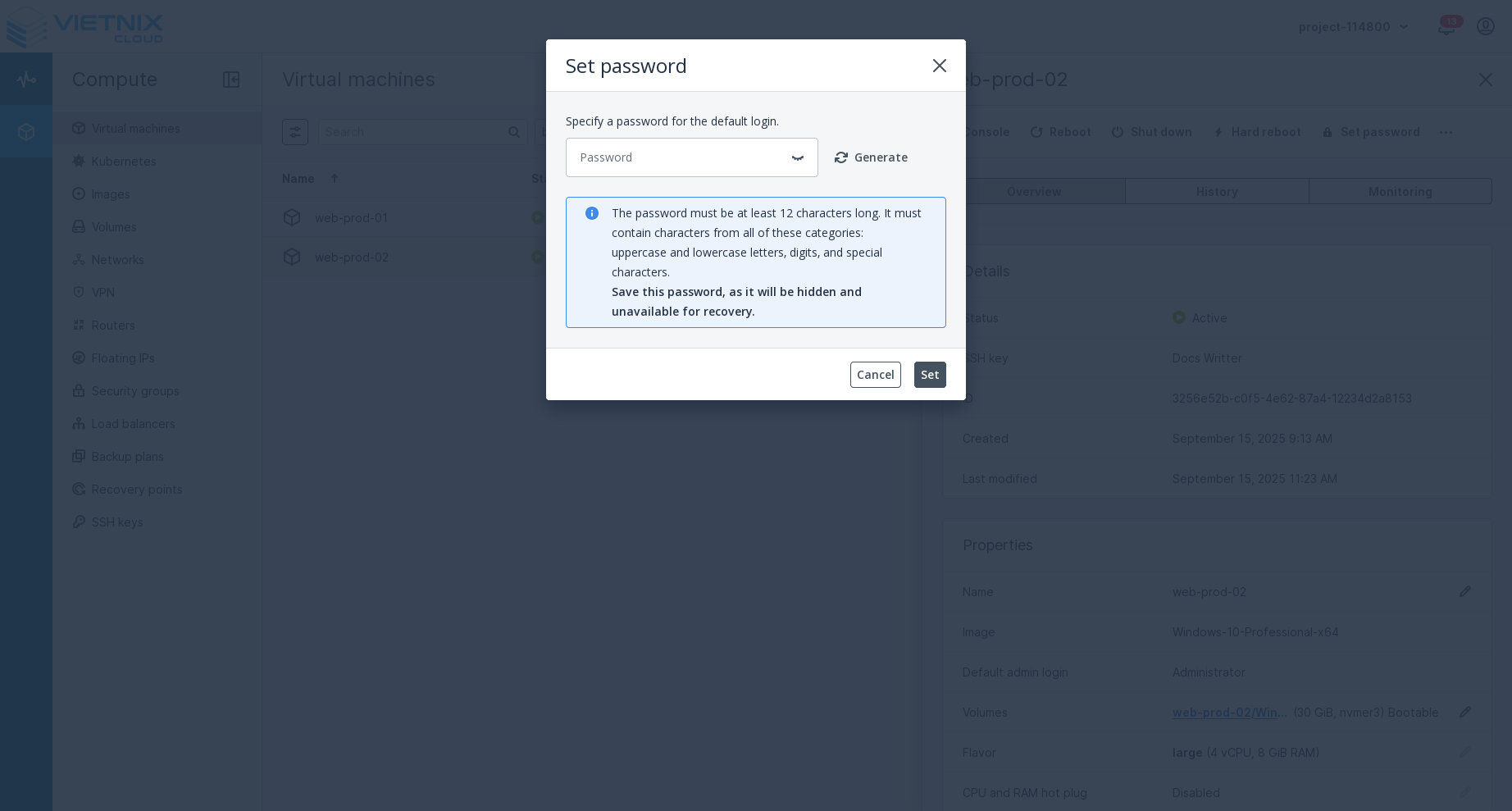 Press the "Set Password" button. This action allows you to set or change the password for the VM. You will be prompted to enter the new password and confirm it before proceeding.
Press the "Set Password" button. This action allows you to set or change the password for the VM. You will be prompted to enter the new password and confirm it before proceeding.
Set password for Linux VM only supports setting the password for the root user. For Windows VM, it supports setting the password for the Administrator user.
Set password will apply the new password immediately. You don't need to reboot the VM.
Enter rescue mode
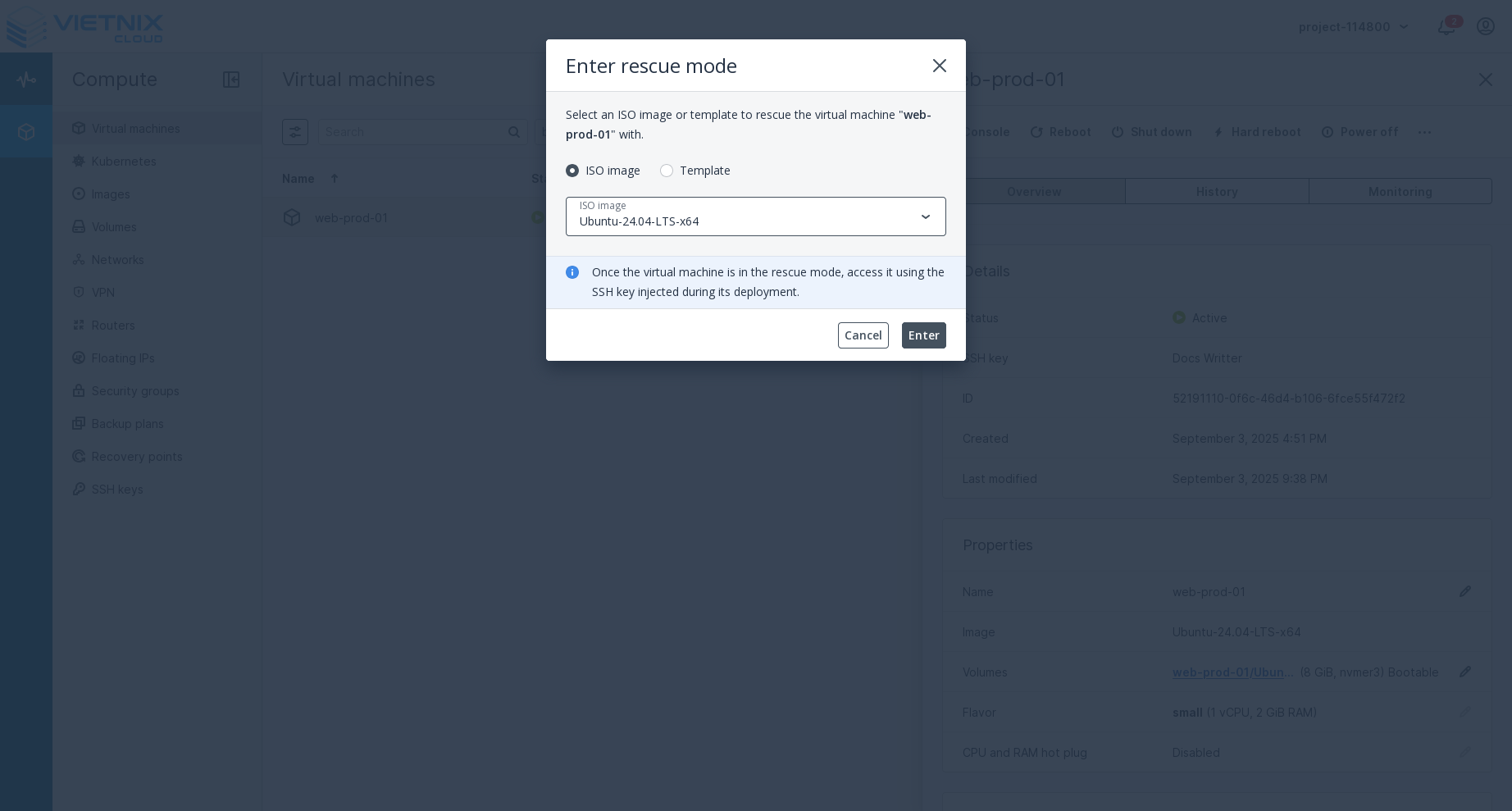 Press the "Enter Rescue Mode" button. This action will boot the VM into rescue mode, which is a minimal environment used for troubleshooting and repairing issues with the VM's operating system. You will be prompted to select a rescue image/template before proceeding.
Press the "Enter Rescue Mode" button. This action will boot the VM into rescue mode, which is a minimal environment used for troubleshooting and repairing issues with the VM's operating system. You will be prompted to select a rescue image/template before proceeding.
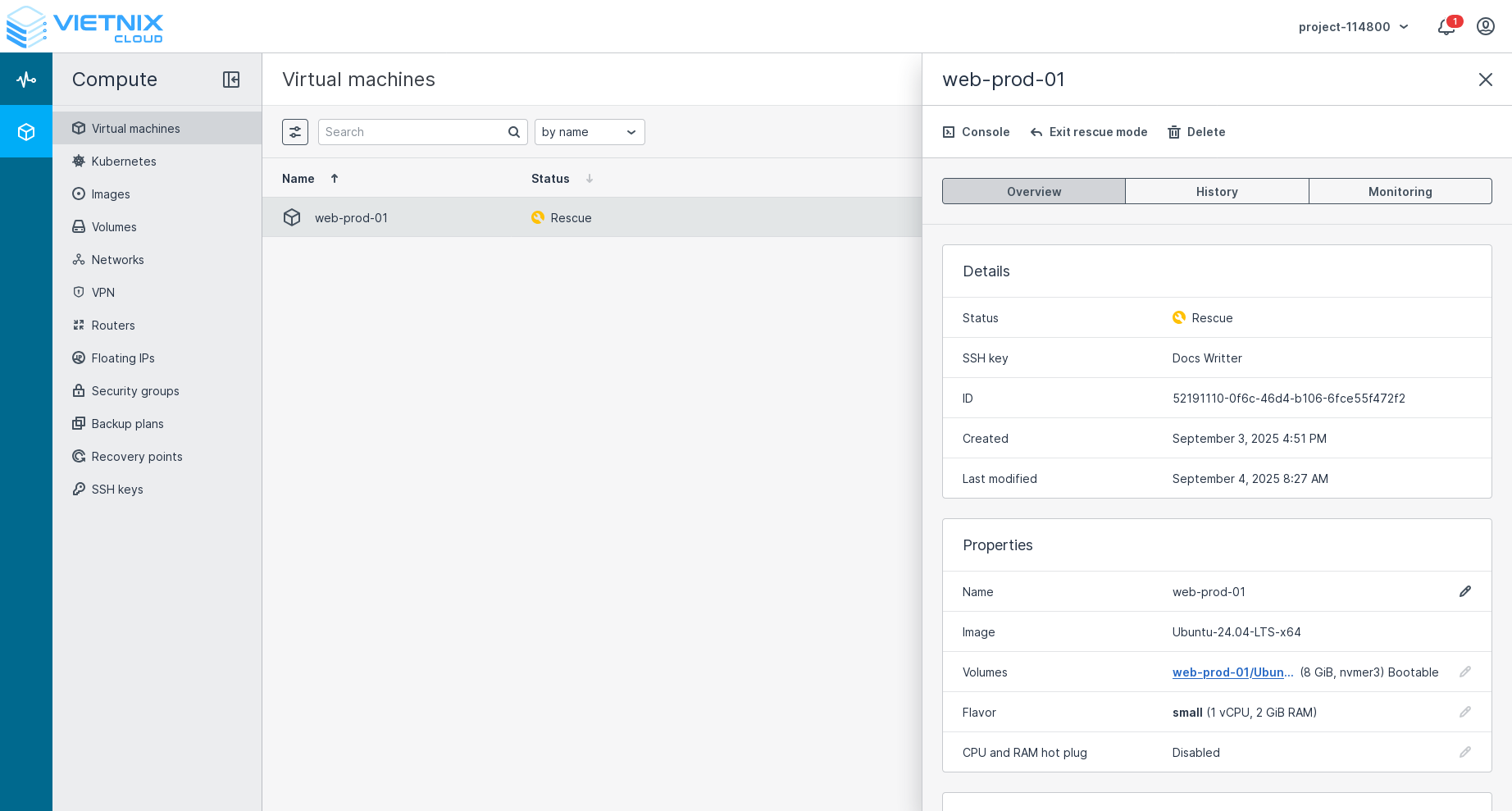 After entering rescue mode, you can access the VM's console to perform necessary repairs or diagnostics.
After entering rescue mode, you can access the VM's console to perform necessary repairs or diagnostics.
Entering rescue mode will temporarily make the VM unavailable for normal operations. Ensure you have saved any important data before proceeding. Exiting rescue mode will reboot the VM, which may lead to data loss if there are unsaved changes.
Download console log
The "Download console log" action allows you to retrieve the VM's console output as a text file. This log contains boot messages, system logs, and other console output that can be valuable for troubleshooting issues with your VM.
To download the console log:
- Select the VM from your instances list
- Click on the "Download console log" option from the actions menu
- The log file will be downloaded to your local machine
Console logs are particularly useful when a VM is not booting properly or is experiencing issues that prevent normal access. They can help identify boot failures, kernel panics, or other system-level problems.
Delete
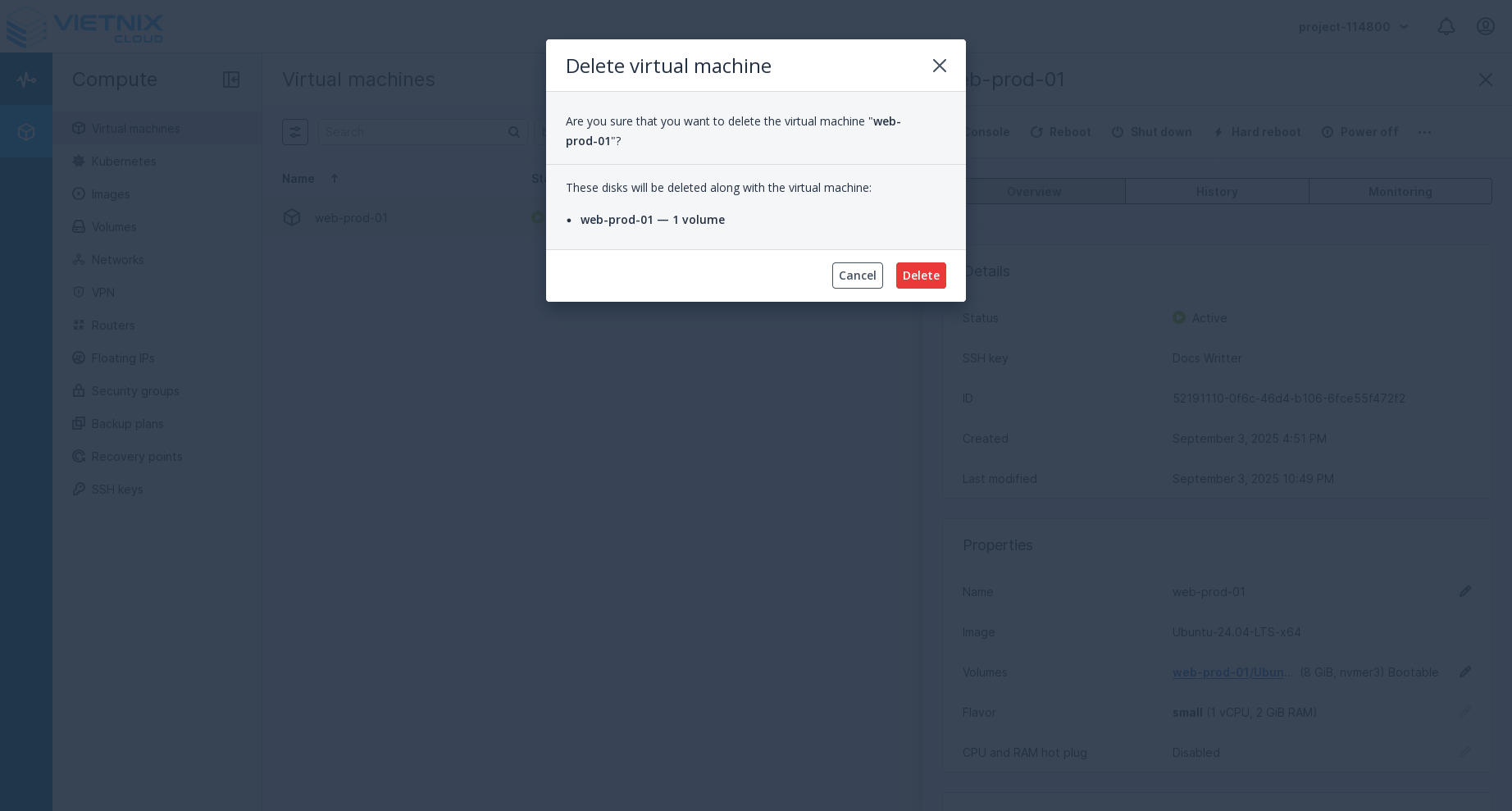 Press the "Delete" button. This action will permanently delete the VM. You will be prompted to confirm the deletion before proceeding.
Press the "Delete" button. This action will permanently delete the VM. You will be prompted to confirm the deletion before proceeding.
Related Resources
- Remote Access - Learn how to connect to and interact with your virtual machine's console
- Monitoring VM - Discover tools and techniques for monitoring your virtual machine's performance